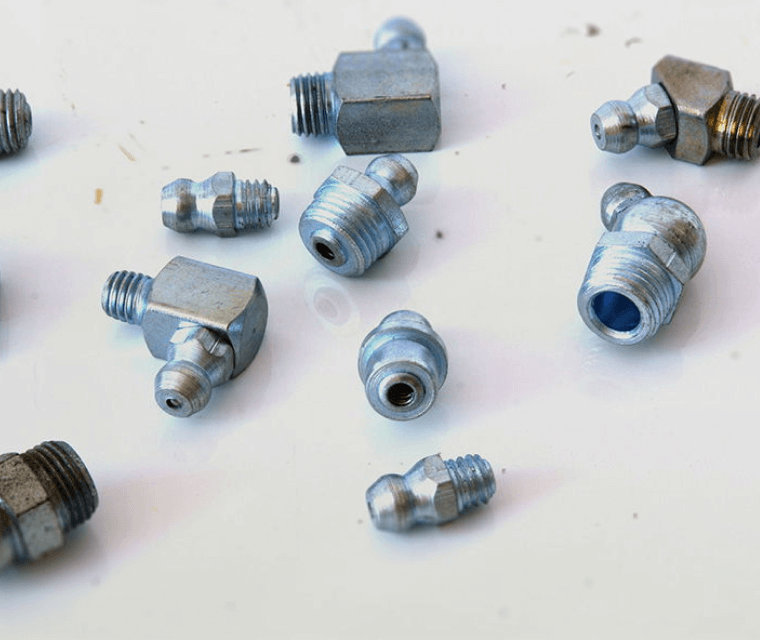
Grease Nipple in Vatva
Hex bolts, also known as hex cap screws or machine bolts, are widely used fasteners in industries such as construction, machinery, automotive, and heavy equipment. They come in various types based on threading, material, finish, head style, and standards. Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the right bolt for specific applications.
1. Based on Thread Type
Fully Threaded Hex Bolts
Threads run the entire length of the bolt, providing maximum grip strength.
- Threads run along the entire length of the bolt.
- Provides maximum grip strength.
- Ideal for applications where tension is critical.
Partially Threaded Hex Bolts
The shank (non-threaded portion) provides shear strength, making them ideal for structural applications.
- Smooth shank portion for better shear resistance.
- Threaded end for secure fastening.
- Ideal for applications requiring strength along the shank.
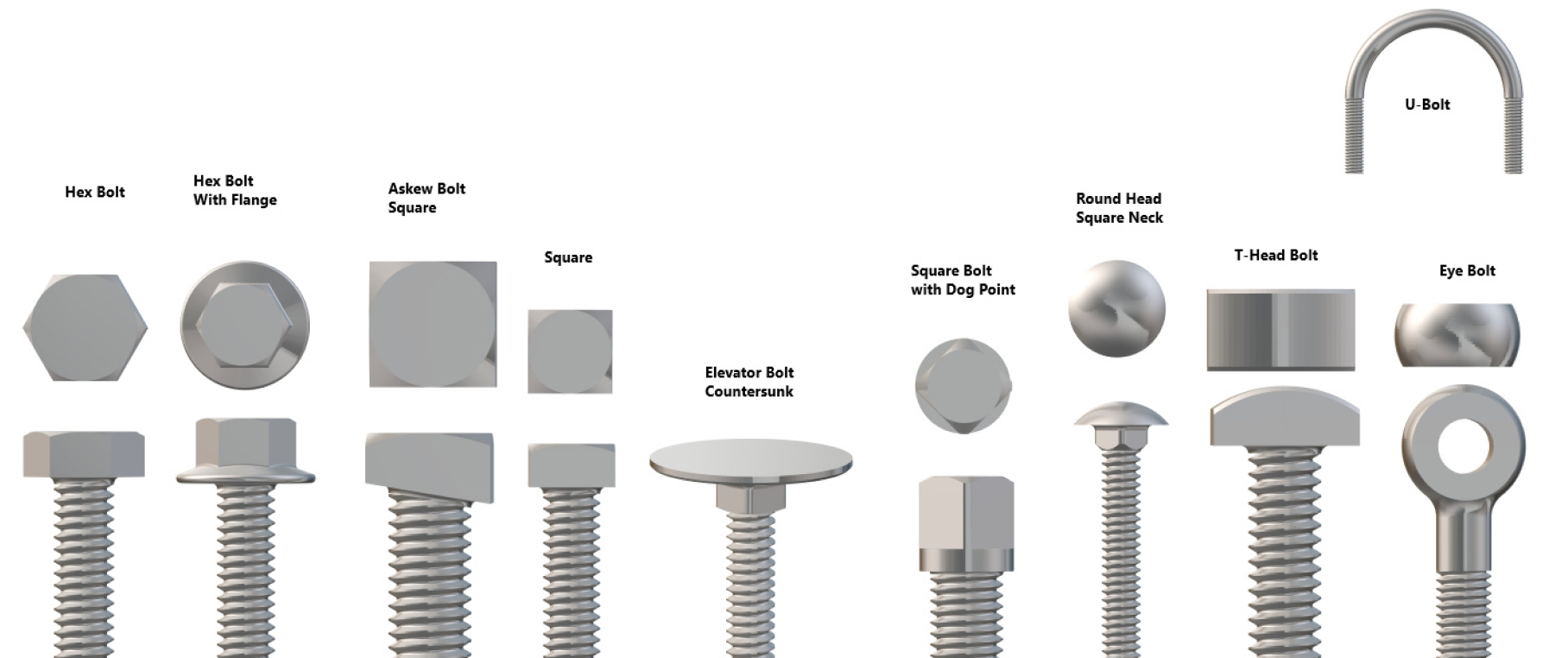
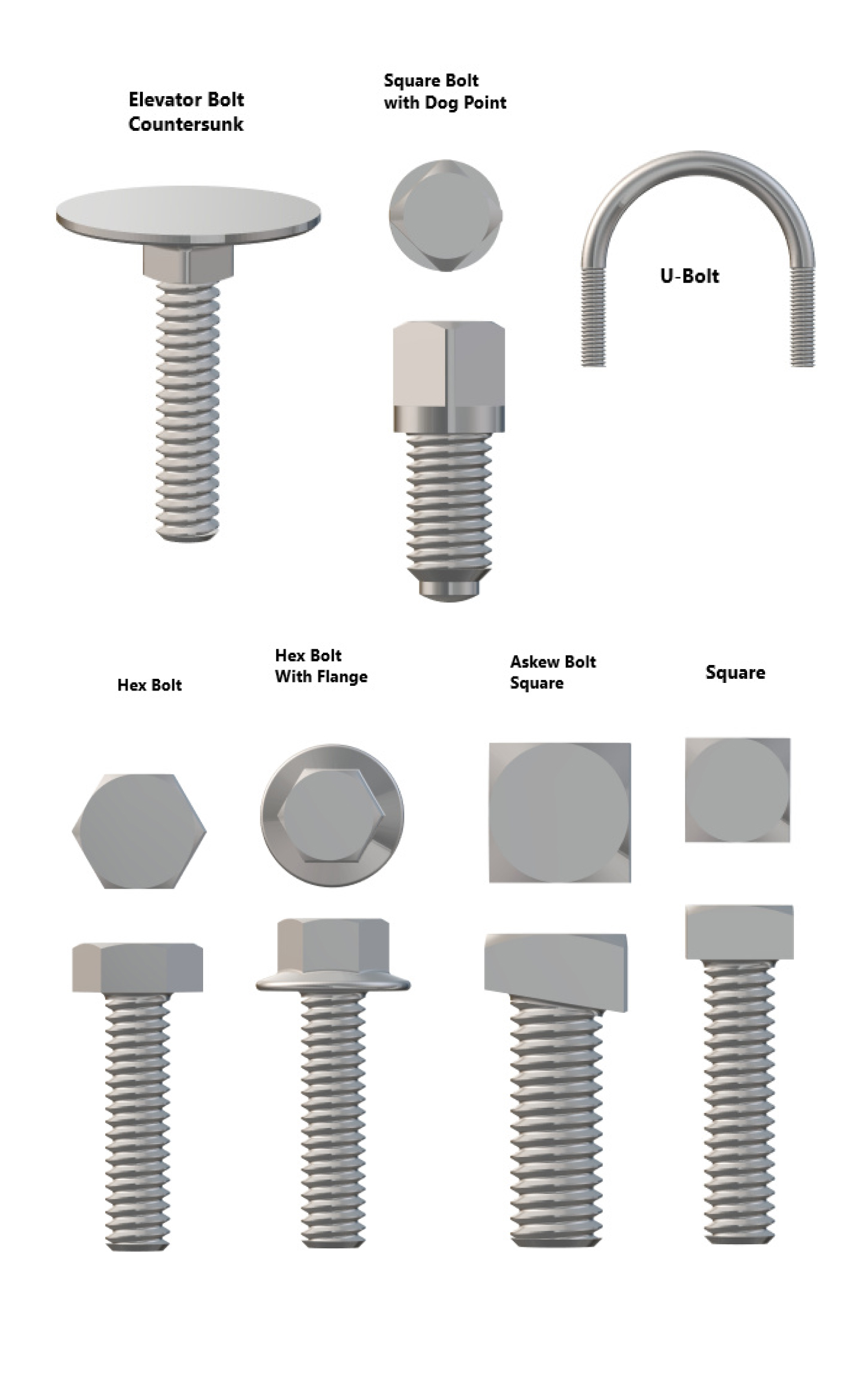
2. Based on Head Style
- Standard Hex Head Bolts: Most common; six-sided head used with a wrench or socket.
- Flange Hex Bolts: Built-in washer under the head for better load distribution.
- Heavy Hex Bolts: Larger and thicker head for structural steel connections.
- Hex Tap Bolts: Fully threaded with a hex head; often used in tapped holes.
3. Based on Material
- Carbon Steel: Most common; available in various grades.
- Stainless Steel: Corrosion-resistant; common grades include 304 and 316.
- Alloy Steel: High strength; used in heavy-duty applications.
- Brass / Bronze: Decorative or non-magnetic; good corrosion resistance.
- Titanium: Lightweight, strong, and corrosion-resistant; used in aerospace and medical applications.
4. Based on Finish / Coating
- Zinc-Plated: Provides mild corrosion resistance.
- Hot-Dip Galvanized: Heavy-duty corrosion resistance; suitable for outdoor/marine use.
- Black Oxide: Minimal corrosion resistance; used for appearance.
- Phosphate Coated: Improves paint adhesion and lubricity.
5. Based on Standards
- ASTM A307 / A325 / A490: U.S. structural standards for various bolt grades.
- ISO / DIN: Metric standards: DIN 931 for partially threaded bolts, DIN 933 for fully threaded bolts.
- BS (British Standards): Common in the UK and former colonies.
6. Specialty Hex Bolts
- Structural Hex Bolts: Heavy-duty, high-strength bolts used in steel-to-steel connections.
- Metric Hex Bolts: Specified by diameter and pitch in millimeters.
- Shoulder Bolts (Stripper Bolts): Feature a smooth shoulder under the head for rotating or sliding parts.
Conclusion
Selecting the right type of hex bolt is vital for the success of any project. Consider thread type, head style, material, finish, and standards to ensure maximum performance and longevity. High-quality hex bolts are essential for construction, machinery, automotive, and engineering applications.
Recent Blogs